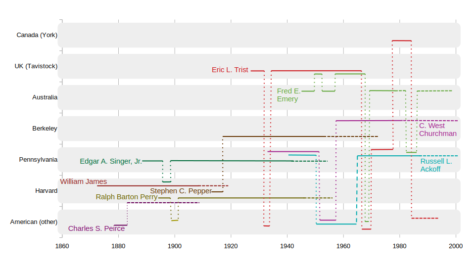
Digging into philosophies underlying the systems sciences, pragmatism seems to have been a strong historical foundation for some research streams. In ongoing discussions, Gary Metcalf and I have been approaching pragmatism from two directions. Gary has been tracking from mid-1800s forward, listening to the audiobook The Metaphysical Club, with a history of figures living through the American Civil War, seeking alternative approaches to the British and continental European ideas. I have been working backwards on two streams. (1) West Churchman and Russell Ackoff were students of Edgar A. Singer Jr., who was a father of a pragmatic school of thought at the University of Pennsylvania, having previously taught with William James at Harvard University. (2) Eric Trist and Fred Emery, in the development of the Socio-Ecological Systems perspective, track back to Stephen C. Pepper, who studied under Ralph Barton Perry, an associate of William James who is recognized for anthologizing and clarifying James’ writing.
The ISSS Kruger Park 2023 meeting was an opportunity for us to share our work in progress. Tracing the institutional lineages of some of the key figures of interest shows periods when the philosophers and systems scientists had formal appointments to the same places.
Notable institions include Harvard U., U. Pennsylvania, and the Tavistock Institute for Human Relations. The many decades give a sense of the time scales (e.g. Pepper arrived at U.C. Berkeley much before Churchman; Trist and Emery were together at Tavistock, and visited Ackoff at U.… Read more (in a new tab)
Digging into philosophies underlying the systems sciences, pragmatism seems to have been a strong historical foundation for some research streams. In ongoing discussions, Gary Metcalf and I have been approaching pragmatism from two directions. Gary has been tracking from mid-1800s forward, listening to the audiobook The Metaphysical Club, with a history of figures living through the American Civil War, seeking alternative approaches to the British and continental European ideas. I have been working backwards on two streams. (1) West Churchman and Russell Ackoff were students of Edgar A. Singer Jr., who was a father of a pragmatic school of thought at the University of Pennsylvania, having previously taught with William James at Harvard University. (2) Eric Trist and Fred Emery, in the development of the Socio-Ecological Systems perspective, track back to Stephen C. Pepper, who studied under Ralph Barton Perry, an associate of William James who is recognized for anthologizing and clarifying James’ writing.
The ISSS Kruger Park 2023 meeting was an opportunity for us to share our work in progress. Tracing the institutional lineages of some of the key figures of interest shows periods when the philosophers and systems scientists had formal appointments to the same places.
Notable institions include Harvard U., U. Pennsylvania, and the Tavistock Institute for Human Relations. The many decades give a sense of the time scales (e.g. Pepper arrived at U.C. Berkeley much before Churchman; Trist and Emery were together at Tavistock, and visited Ackoff at U.… Read more (in a new tab)