An article on “sciencing and philosophizing”, coauthored by Gary S. Metcalf and myself, has been published in the Journal of the International Society for the Systems Sciences, following the ISSS 2023 Kruger Park conference in South Africa, last July. There’s a version cacned on the Coevolving Commons.
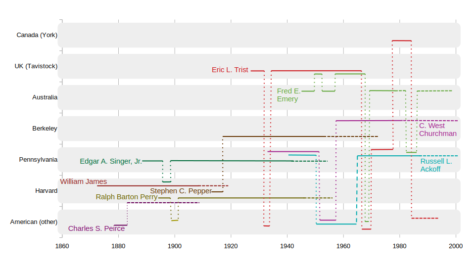
This article started in a series of conversations with Gary in early 2023, as he was listening to the history of Pragrmatism as an audiobook of The Metaphysical Club: A Story of Ideas by Louis Menand, written in 2002. Key figures in the development of this philosophy includes William James (1842—1910) and Charles Sanders Peirce (1839—1914). My interests have taken me backwards in time, with C. West Churchman and Russell Ackoff both students of Edgar A. Singer, Jr., who was a student of William James. A thread looking into Stephen C. Pepper, also a student of William James and Ralph Barton Perry, was encouraged by online comments from Michael C. Jackson, OBE. This led to a tracing of philosophical influences from the 1890s to 2000.
With my current research into Classical Chinese philosophy, I was encouraged by an 1993 interview citing Churchman having a similar interest for in exploring alternatives to classical Western philosophy for sciencing on systems.
… Read more (in a new tab)In conversations with Churchman on the historical sources of systems thinking, he often identified the Chinese I Ching as the oldest systems approach. As an effort to model dynamic processes of changing relationships between different kinds of elements, the I Ching might be seen as a systemic approach, in contrast with the more systematic approach of rationalist Western thought, rooted in the work of Plato and Aristotle.
An article on “sciencing and philosophizing”, coauthored by Gary S. Metcalf and myself, has been published in the Journal of the International Society for the Systems Sciences, following the ISSS 2023 Kruger Park conference in South Africa, last July. There’s a version cacned on the Coevolving Commons.
This article started in a series of conversations with Gary in early 2023, as he was listening to the history of Pragrmatism as an audiobook of The Metaphysical Club: A Story of Ideas by Louis Menand, written in 2002. Key figures in the development of this philosophy includes William James (1842—1910) and Charles Sanders Peirce (1839—1914). My interests have taken me backwards in time, with C. West Churchman and Russell Ackoff both students of Edgar A. Singer, Jr., who was a student of William James. A thread looking into Stephen C. Pepper, also a student of William James and Ralph Barton Perry, was encouraged by online comments from Michael C. Jackson, OBE. This led to a tracing of philosophical influences from the 1890s to 2000.
With my current research into Classical Chinese philosophy, I was encouraged by an 1993 interview citing Churchman having a similar interest for in exploring alternatives to classical Western philosophy for sciencing on systems.
… Read more (in a new tab)In conversations with Churchman on the historical sources of systems thinking, he often identified the Chinese I Ching as the oldest systems approach. As an effort to model dynamic processes of changing relationships between different kinds of elements, the I Ching might be seen as a systemic approach, in contrast with the more systematic approach of rationalist Western thought, rooted in the work of Plato and Aristotle.