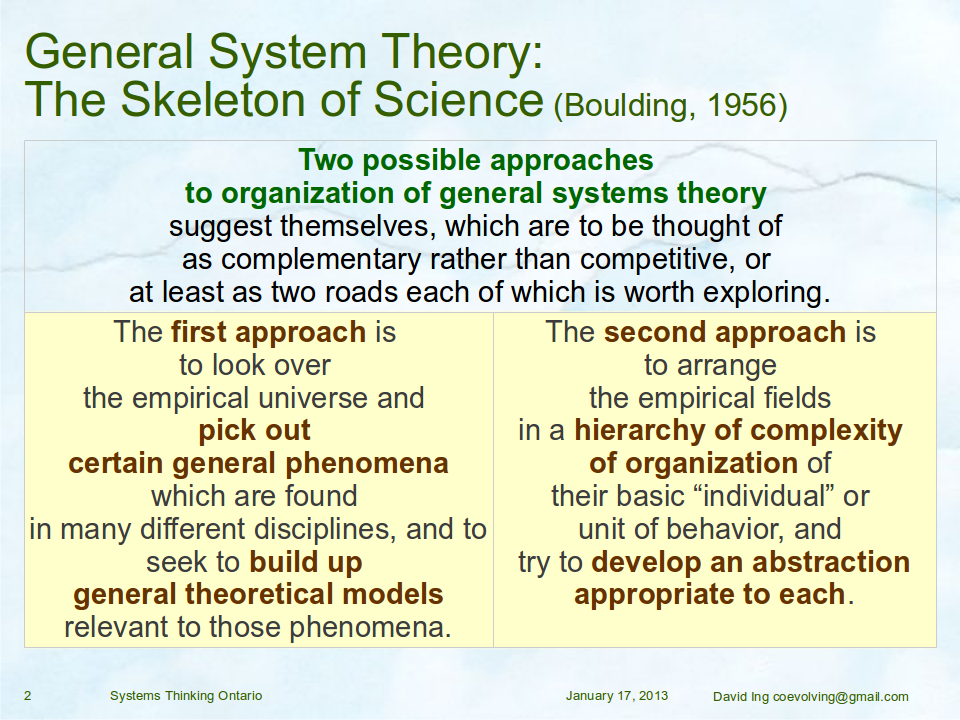
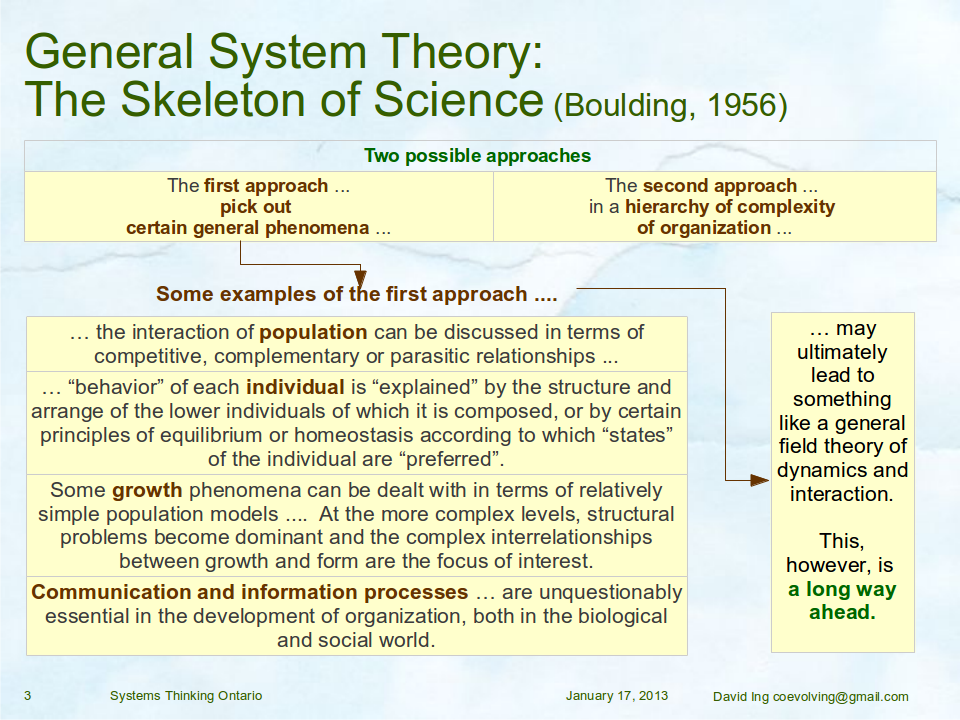
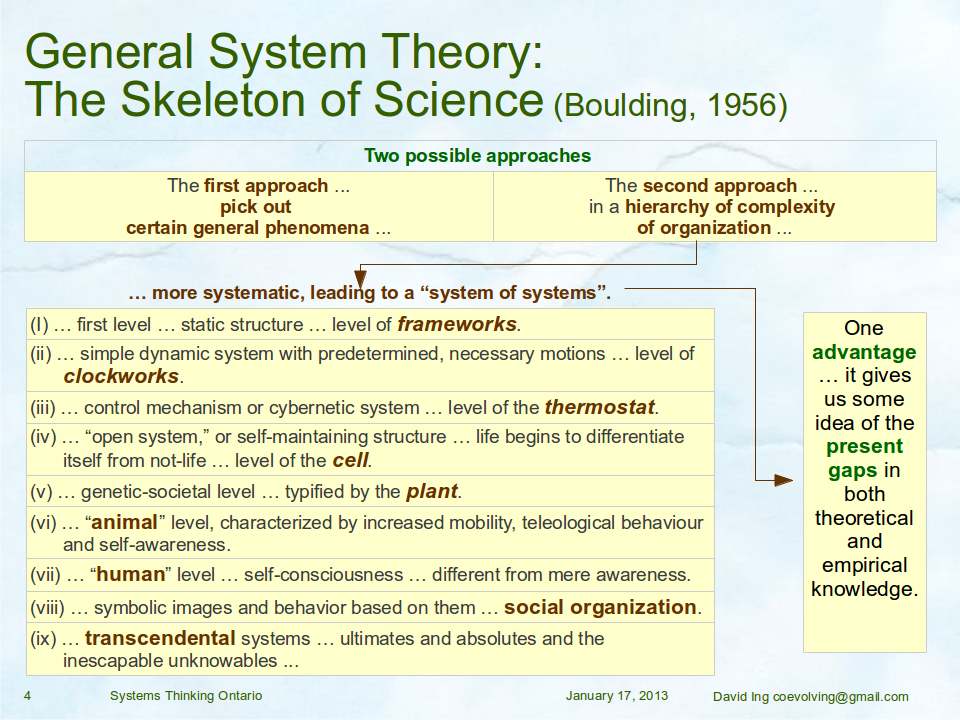
A meeting of systems scientists and systems engineers together as the Systems Science Working Group at the INCOSE International Workshop 2014 provided a forum for “a proposal for collaboration on a pattern language for service systems (science, management, engineering and design)”. The title is deliberately long, and required some hours to unpack the content in the slide deck.
The initiative has been presented as ambitious. Writing a (good) pattern language is non-trivial. The originator of the pattern language, Christopher Alexander, published his first work in 1968, and then spent 9 years in collaboration until the 1977 release of the landmark A Pattern Language: Towns, Building, Construction. In a 2010 interview, Alexander was asked about his perception on similar efforts.
… Read more (in a new tab)[Rob Hoskins]: What’s been your opinion of subsequent peoples’ attempts at doing Pattern Languages – I’ve seen a couple of different ones, have you seen many?
[Christopher Alexander]: Some. They’re not that good. The reason I say that is that the people who’ve attempted to work with Pattern Languages, think about them, but are not conscious of the role of morphological elegance in the unfolding. In a biological case, they always are elegant and the unfolding morphology is a sort of magic. But it’s very simple. It’s not as if it’s magic because it’s complicated, it’s just … like that.
[Rob Hoskins]: I guess when we were talking before about how a Pattern Language goes from the large down to the small, maybe when we were talking about it as going outwards maybe it is more like an unfolding process?